This is the quickest and easiest SSL install for Proxmox I could find. Great little tutorial.

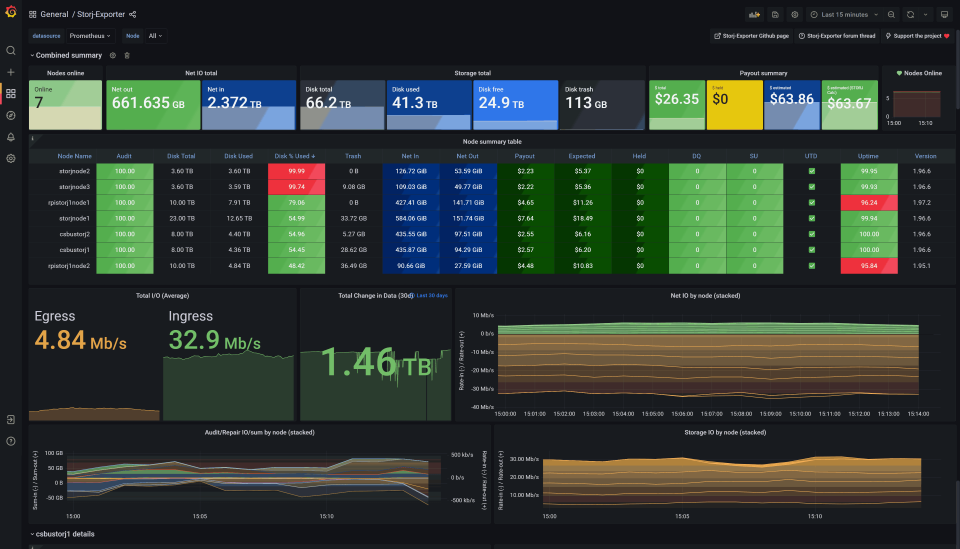
PC Diagnostic Tools
OCCT – Check voltages, temperatures, loads, etc.. All around fantastic diagnostic tool.
HWiNFO – Another good tool for monitoring your system.
DNS Benchmark – Checking DNS info
CPUZ – is a freeware that gathers information on some of the main devices of your system
List of Cell Carrier Email to Text SMS
Email to SMS Gateways
T-Mobile – number@tmomail.net
Virgin Mobile – number@vmobl.com
AT&T – number@txt.att.net
Sprint – number@messaging.sprintpcs.com
Verizon – number@vtext.com
Tracfone – number@mmst5.tracfone.com
Ting – number@message.ting.com
Boost Mobile – number@myboostmobile.com
U.S. Cellular – number@email.uscc.net
Metro PCS – number@mymetropcs.com
Sound Switch
*UPDATE* Application no longer opens in Windows 11, seems to be very little support. I have since uninstalled this application and am now using Audio Switcher
Toggle your speakers to headphones with Sound Switch.
Installing Windows 11 VM in ESXI 7.0
Found this fix for “This PC Can’t run Windows 11 — The PC doesn’t meet the minimum requirements to install this version of Windows”
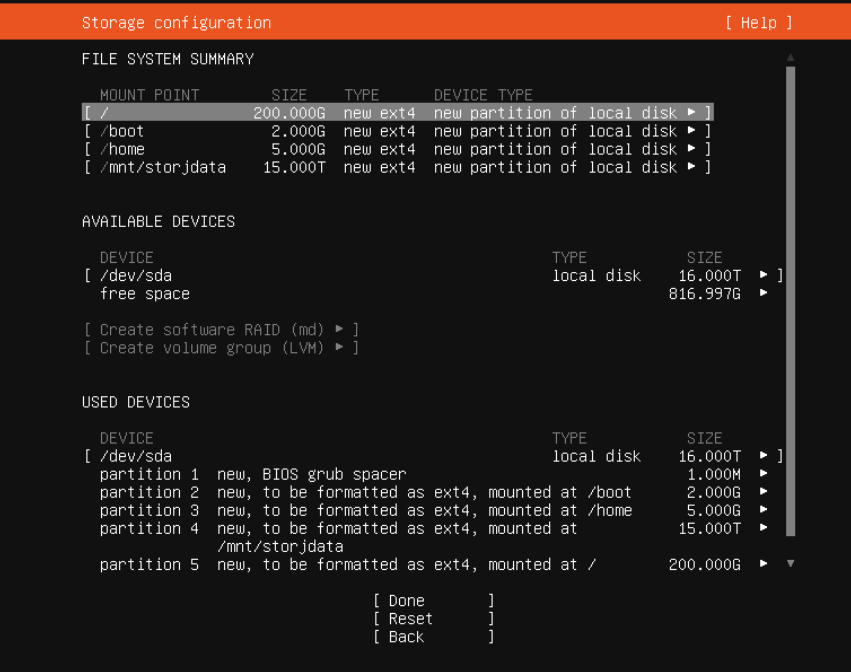
Resize Ubuntu LVM Partition
Ensure the VM has the capacity to expand (ESXI)
sudo lvdisplay
sudo lvextend -L 2T /dev/ubuntu-vg/lv-0